Introduction to Cybersecurity
In today’s connected world, everything — from smartphones and laptops to banks, schools, and hospitals — relies on the internet. But as our digital dependence grows, so do the cyber threats that target our personal and professional lives.
That’s where Cybersecurity plays a crucial role. Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computers, networks, servers, and data from malicious attacks, theft, and damage. It ensures that your information stays safe, private, and accessible only to authorized users.
To fight these threats, we need Cybersecurity — a system of protection designed to keep our digital world safe.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to a set of technologies, processes, and best practices designed to protect systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access or damage. It involves defending individuals and organizations against cyber threats like malware, phishing, ransomware, and hacking.
Definition:
Cybersecurity is the protection of digital systems, devices, and data from cyber threats and online attacks.
In simple words, it’s everything we do to secure our digital life — from using strong passwords to building firewalls and encrypted networks.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Cybersecurity is not just for large companies — it’s essential for everyone using the internet. Here’s why:
- 🔐 Data Protection: Keeps your personal, financial, and business information safe from hackers.
- 🧾 Privacy: Protects your identity and sensitive online records from being misused.
- 💰 Financial Security: Prevents losses from scams, fraud, and ransomware attacks.
- ⚙️ Business Continuity: Ensures your systems and websites stay operational without downtime.
- 🏛 National Security: Defends critical infrastructure such as defense systems, power grids, and communication networks from cyber warfare.
In short, cybersecurity helps build trust, reliability, and safety in our digital environment.
How Cybersecurity Works
Cybersecurity uses a combination of technologies, tools, and processes to protect digital assets.
Here’s how it works:
- Prevention – Using firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption to block attacks.
- Detection – Monitoring networks and systems for suspicious activity.
- Response – Taking quick action to minimize damage after an attack.
- Recovery – Restoring data and services after an incident.
Types of Cybersecurity
1. Network Security
Network Security protects an organization’s internal network from unauthorized access, misuse, or attacks.
It ensures that only legitimate users and data traffic are allowed through.
🔹 Examples:
- Firewalls
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Network Access Control (NAC)
🧠 Goal:
To prevent hackers, malware, or data breaches from entering or spreading through your network.
2. Information Security (InfoSec)
Information Security focuses on protecting data — both stored (at rest) and in transit (when being shared).
It ensures that information remains confidential, accurate, and available.
🔹 Key Principles (CIA Triad):
- Confidentiality – Only authorized people can access data.
- Integrity – Data remains unchanged and accurate.
- Availability – Data is available when needed.
🔹 Examples:
- Data encryption
- Access control policies
- Secure backups
3. Application Security
Application Security protects software and apps from cyber threats during development and use.
Attackers often target applications to steal user data or disrupt services.
🔹 Techniques:
- Input validation
- Secure coding practices
- Regular security testing (SAST, DAST)
- Use of Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
🔹 Examples:
- Preventing SQL Injection or Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
🧠 Goal:
To ensure that applications are secure, updated, and free from vulnerabilities.
4. Cloud Security
Cloud Security focuses on protecting data, applications, and systems hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Since more companies store data in the cloud, ensuring security here is essential.
🔹 Measures Include:
- Data encryption
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Regular security audits
🧠 Goal:
To safeguard cloud environments from unauthorized access and data breaches.
5. Endpoint Security
Endpoint Security secures individual devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices.
Each device connected to a network is a potential target for hackers.
🔹 Examples:
- Antivirus software
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) tools
🧠 Goal:
To prevent attacks like malware, ransomware, or phishing from infecting user devices.
6. Operational Security (OpSec)
Operational Security (OpSec) is about managing and protecting sensitive information and access rights within an organization.
It controls how and by whom data can be used or shared.
🔹 Examples:
- Setting user access levels
- Monitoring employee behavior
- Data handling policies
🧠 Goal:
To minimize the risk of insider threats and accidental data leaks.
7. Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity
This type of cybersecurity ensures that an organization can recover quickly after a cyberattack or data loss.
Disaster Recovery focuses on restoring IT systems and data, while Business Continuity ensures that operations continue smoothly during and after an incident.
🔹 Examples:
- Data backups
- Cloud disaster recovery plans
- Incident response procedures
🧠 Goal:
To reduce downtime and restore normal operations as fast as possible.
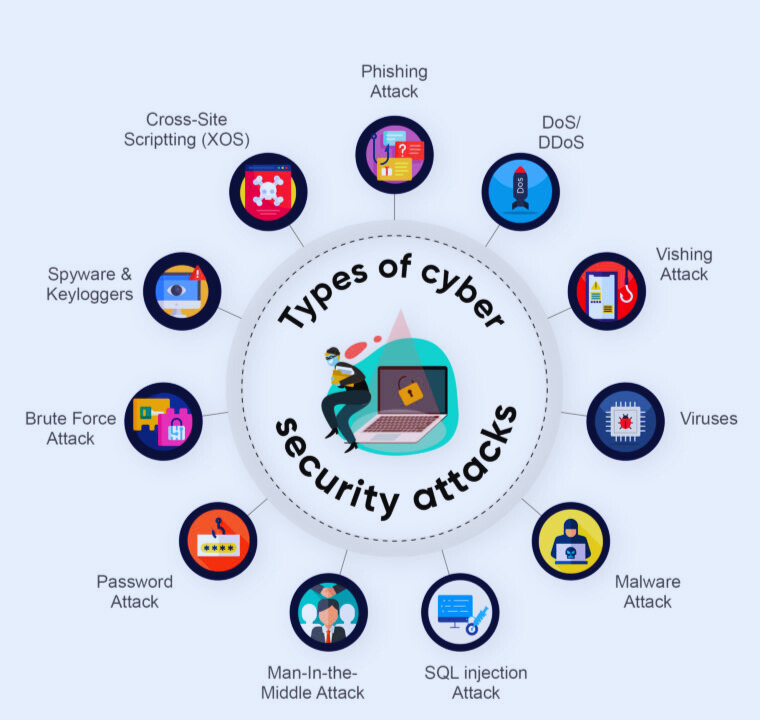
Types of Cyber Attacks
1. Malware Attack
Malware (short for malicious software) is a program or file designed to harm a computer or network.
It can steal data, spy on user activity, or damage files and systems.
Common types of malware:
- Virus: Attaches itself to legitimate files and spreads to other files.
- Worm: Self-replicates and spreads without human action.
- Trojan Horse: Appears as a harmless file or app but gives attackers access to your system.
- Spyware: Secretly monitors user activity and steals information.
- Ransomware: Locks or encrypts files and demands ransom to restore access.
Example:
The WannaCry ransomware attack (2017) infected 200,000+ computers across 150 countries.
2. Phishing Attack
Phishing is a social engineering attack where hackers trick users into revealing personal information such as passwords or credit card details.
How it works:
Attackers send fake emails or messages that look like they’re from trusted organizations (like banks or companies). Clicking links or downloading attachments leads to data theft.
Example:
A fake email from “your bank” asking you to verify account details.
Prevention Tips:
- Never click unknown links.
- Check sender’s email address carefully.
- Use spam filters and multi-factor authentication.
3. Denial-of-Service (DoS) & Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attack
In this attack, hackers flood a network or server with massive traffic to overload it and make it unavailable to legitimate users.
Difference:
- DoS: Single system attacks a server.
- DDoS: Multiple systems attack simultaneously.
Example:
A DDoS attack can shut down an e-commerce website during a big sale.
Protection:
Use firewalls, load balancers, and DDoS mitigation services.
4. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack
In this attack, a hacker secretly intercepts communication between two parties to steal or alter data.
Example:
When using an unsecured Wi-Fi network, a hacker could intercept your login credentials while you access your bank account.
Prevention:
- Avoid public Wi-Fi for financial transactions.
- Use encryption (HTTPS, VPN).
5. SQL Injection Attack
Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in an application’s database layer by inserting malicious SQL queries.
Result:
They can access, modify, or delete data stored in the database.
Example:
An attacker entering malicious code into a login field to bypass authentication.
Prevention:
- Validate all input fields.
- Use parameterized queries.
- Keep databases updated.
6. Social Engineering
Attackers manipulate people into revealing confidential information.
Example: Pretending to be tech support or a company employee to gain trust and access systems.
7. Password Attack
Attackers try to crack passwords using various methods:
- Brute Force Attack: Tries every possible password combination.
- Dictionary Attack: Uses common password lists.
- Credential Stuffing: Uses leaked username-password pairs.
Prevention:
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA).
8. Ransomware Attack
A type of malware that encrypts the victim’s files and demands payment (ransom) for decryption.
Example:
The Petya and WannaCry ransomware attacks.
Prevention:
- Backup your data regularly.
- Don’t click suspicious attachments.
9. Insider Threat
Not all cyberattacks come from outsiders — sometimes, employees misuse their access to steal or damage data.
Example: A worker downloading confidential files before resigning.
10.Spyware and Adware
These programs secretly monitor user activities or display unwanted ads.
Example: Spyware records keystrokes to steal login credentials.
Common Types of Cyber Attacks:
| Attack Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Malware | Harmful software that damages systems | WannaCry, Trojan |
| Phishing | Fake emails to steal data | Bank scam emails |
| DDoS | Overloading a system | Taking down websites |
| MITM | Intercepting communication | Wi-Fi eavesdropping |
| SQL Injection | Injecting malicious code in databases | Website data theft |
| Ransomware | Encrypting files for ransom | Locky, Petya |
| Password Attack | Stealing passwords | Brute force, Credential stuffing |
| Social Engineering | Tricking users | Fake tech support calls |
| Insider Threat | Internal misuse of access | Employee data theft |
| Spyware/Adware | Tracking users or showing ads | Hidden monitoring apps |
🔐 How to Protect Yourself from Cyber Attacks
Here are some basic cybersecurity practices everyone should follow:
- Use strong, unique passwords and update them regularly.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
- Avoid clicking suspicious links or downloading unknown attachments.
- Keep your software and operating system updated.
- Use reliable antivirus and firewall software.
- Regularly backup your data.
- Be careful with what you share online.
🌍 The Future of Cybersecurity
With the rise of AI, IoT, and cloud computing, cybersecurity threats are evolving. The future will rely on AI-based threat detection, Zero Trust architectures, and cyber awareness training for everyone — not just IT professionals.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity isn’t just for companies or experts — it’s essential for everyone who uses the internet. Understanding how attacks happen and how to prevent them is the first step toward a safer digital world.
Whether you’re a student, employee, or business owner, adopting smart cyber habits can protect your data, privacy, and reputation from the growing number of online threats.

