Artificial Intelligence (AI) is shaping the way we live, work, and interact with technology. One of the most fascinating concepts in this field is AI Agents. Whether it’s your virtual assistant like Siri, chatbots on websites, or complex systems in robotics, AI agents are at the heart of it all. In this blog, let’s break down everything you need to know about AI agents—what they are, how they work, and why they matter.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI Agent is a software (or system) that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve a specific goal. Think of it as a smart helper that observes, thinks, and acts—just like humans, but in a digital or robotic form.
AI agents are smart software programs that can work on their own, interact with the environment, make decisions from inputs, and achieve specific goals without constant human control. In simple terms, you can think of an AI agent as a system that can learn, adapt, and act to solve problems or answer queries until the task is completed.
For example, imagine a virtual helper that can handle customer inquiries 24/7, automate repetitive tasks, and make intelligent choices based on the situation. These agents often use machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to understand context, user intent, and provide accurate solutions—just like a human assistant, but much faster.
It’s important to note that AI tools like ChatGPT or Gemini are not full AI agents. They are powerful language models that respond to prompts but don’t act on their own. A true AI agent works independently, using sensors, processors, and decision-making functions, without needing instructions at every step.
👉 Example: Google Maps suggesting the fastest route is an AI agent in action.
Key Functions of Autonomous AI Agents
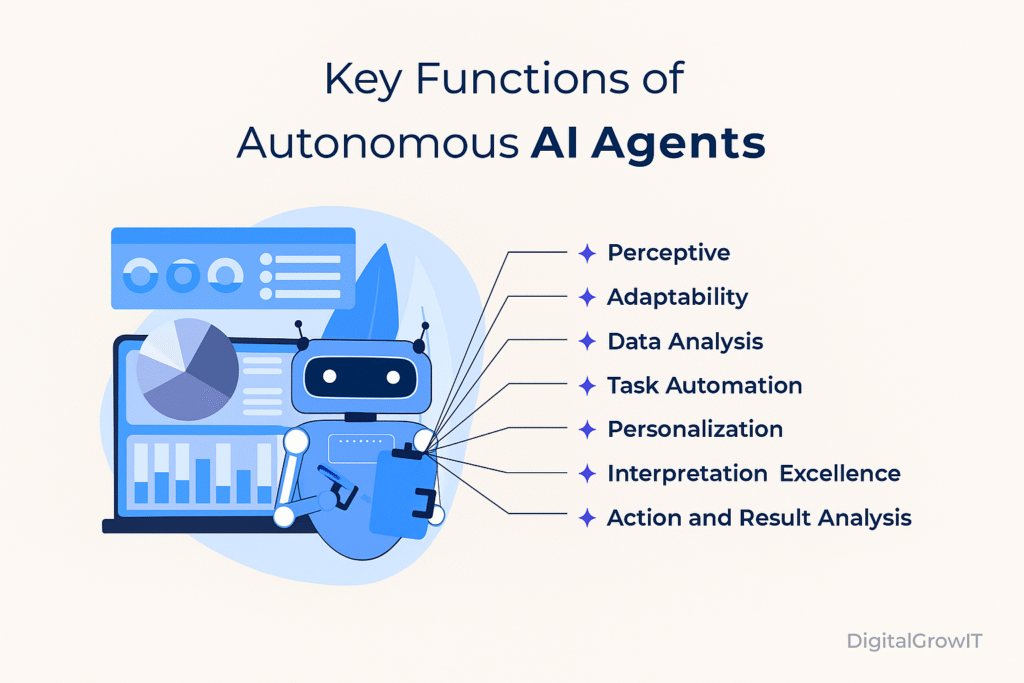
Most software programs or models will function based on their programming and development. But what makes an AI agent different or special to use than other digital entities? Here’s a breakdown of how autonomous AI agents are more powerful, intelligent, and reliable.
Perceptive: AI agents can gather information from different sources like text, voice, or sensors. They notice changes in things like customer behavior or market trends and make smart decisions quickly.
Adaptability: These agents learn from experience and new data. With each interaction, they get better at solving problems and making decisions.
Data Analysis: AI agents handle large amounts of data, find patterns, and give useful insights to support better decision-making.
Task Automation: They can take over repetitive and boring tasks, allowing people to focus on more important work. This saves time and improves efficiency.
Personalization: AI agents can provide services tailored to each person’s preferences and needs, improving customer experience and satisfaction.
Interpretation: They understand and analyze complex data such as text, images, audio, and video. This helps them extract valuable insights and act more effectively.
Action & Results: AI agents aim to achieve set goals. They choose the best actions, review the results, and adjust if things don’t go as planned.
How Do AI Agents Work?
AI agents follow a simple loop:
1.Perception → They collect data from the environment (via sensors, inputs, or APIs).
2.Decision-Making → They process the information using AI/ML algorithms.
3.Action → They perform an action (reply, suggest, automate, move a robot, etc.).
4.Learning → They improve performance by analyzing past outcomes.
👉 Example: A chatbot perceives a customer’s query, decides the best response, sends the reply, and learns from customer feedback to improve future answers.
Tools for Building AI Agents
If you’re curious about building or experimenting with AI agents, here are some popular tools and frameworks:
LangChain – For building conversational AI and autonomous agents.
AutoGPT / BabyAGI – Open-source AI agents that automate tasks.
OpenAI API – For creating intelligent chatbots and assistants.
Rasa – An open-source framework for conversational AI.
Microsoft Bot Framework – For enterprise-grade AI bots.
TensorFlow & PyTorch – For deep learning-based intelligent agents.
Architecture of an AI Agent
The architecture of an AI Agent usually includes these components:
1.Perception Module – Gathers data (sensors, inputs, APIs).
2.Knowledge Base – Stores information, rules, and learned patterns.
3.Decision-Making Engine – Uses AI/ML algorithms to decide what to do.
4.Action Module – Executes actions (text, speech, movements, automation).
5.Learning Module – Continuously updates skills using machine learning.
This modular setup ensures that agents can adapt, learn, and perform efficiently.
Types of AI Agents:
Now that we understand how AI agents work, it’s important to note that not all of them are the same. Different types of AI agents have unique strengths and are designed for specific tasks. Below are three key types of AI agents that businesses can use based on their needs.
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These agents work only when a specific condition or trigger occurs. They follow predefined rules and do not learn from past experiences. Their role is limited to handling basic, repetitive actions.
Best For: Simple tasks that don’t need complex thinking. Examples include digital thermostats that switch on the heater when the temperature drops or password reset systems that react to certain keywords in a user’s request.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These are more advanced than simple reflex agents. They maintain an internal state, allowing them to “remember” and understand how their actions impact the environment. By analyzing past data and outcomes, they make more informed decisions.
Best For: Smart systems that need to analyze historical data. For example, inventory management tools that predict customer demand based on purchase history.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents focus on achieving specific objectives. They compare different options, plan steps, and choose the best strategy to reach a defined goal. This makes them suitable for tasks that require higher reasoning and decision-making.
Best For: Complex activities where outcomes are critical. A good example is self-driving cars, which evaluate different routes and actions to reach a destination safely.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents are designed to choose the best possible action by comparing outcomes. They don’t just follow rules but evaluate which decision provides the greatest benefit or satisfaction for the user.
Best For: Recommending options that balance different needs, such as finding flight tickets that fit both budget and travel time preferences.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents continuously improve by learning from their environment, past experiences, and user interactions. They test their actions, analyze results, and adapt over time to perform tasks more effectively. This makes them smarter and more efficient with each interaction.
Best For: E-commerce platforms that use recommendation systems to better understand customer preferences and deliver more personalized suggestions.
6. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Multi-agent systems involve several agents working together, either independently or in collaboration, to solve complex problems. Each agent has a role, and by communicating with one another, they can handle larger tasks that a single agent cannot manage alone.
Best For: Supply chain management, where different agents handle separate parts of the process and work in sync to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
7. Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical agents are structured like a team with different levels. High-level agents break down big, complex goals into smaller tasks and assign them to lower-level agents. Each agent works on its specific part, and together they complete the overall task efficiently.
Best For: Large organizations that need to manage multiple layers of tasks, projects, and priorities at the same time
Industry-Specific Use Cases of AI Agents
Artificial Intelligence agents are transforming industries by enhancing decision-making, automating tasks, and providing personalized solutions. Here’s how different sectors are leveraging various types of AI agents:
Healthcare – Learning Agents
In healthcare, learning agents play a critical role in improving patient outcomes.
- Creating personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
- Offering predictive diagnostics to detect diseases early.
- Enabling real-time patient monitoring for better care.
Finance – Utility-Based Agents
Finance heavily relies on utility-based agents to analyze large volumes of data and maximize value.
- Real-time fraud detection to safeguard transactions.
- Providing personalized financial advice to customers.
- Automated loan processing for faster approvals.
E-Commerce – Simple Reflex Agents
E-commerce uses simple reflex agents to enhance customer journeys.
- Providing 24/7 customer support through chatbots.
- Personalized product recommendations to boost sales.
- Streamlined checkout processes for better user experience.
Education – Hierarchical Agents
Education systems benefit from hierarchical agents to handle layered tasks.
- Designing personalized learning paths for students.
- Automated grading systems to save time for educators.
- Virtual classes to make learning accessible anywhere.
Manufacturing – Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Manufacturing benefits from multi-agent systems that work together to improve efficiency.
- Supply chain optimization for seamless production.
- Predictive maintenance to reduce downtime.
- Automated quality control for consistent output.
Final Thoughts✨
AI agents are no longer just futuristic concepts—they are part of our everyday lives. From voice assistants to smart customer support bots and self-driving cars, these intelligent systems are changing the way we interact with technology.
As businesses and individuals continue to embrace AI, understanding AI agents is crucial for innovation, efficiency, and staying ahead in the digital age.

